In structural design, waterproofing represents one of the more challenging aspects. It demands high standards in terms of design approach, manufacturing techniques, and precision control. Here, I would like to share some common approaches to waterproofing design.
Common waterproofing methods include the use of rubber rings, two-color injection molding, ultrasonic welding, glue filling, glue application, double-sided adhesive, waterproof and breathable membranes, as well as nano-coating techniques.

Key points of the waterproof design
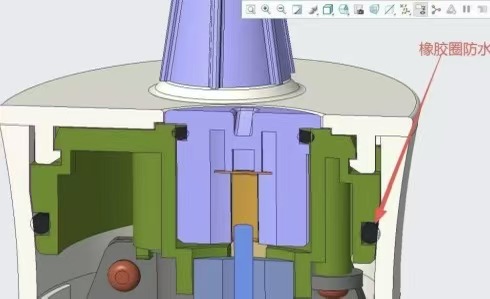
For the waterproofing of the upper and lower casings, if disassembly and maintenance in the future are taken into consideration, a positive-pressure silicone ring design is generally adopted. The hardness of the silicone ring typically falls within the range of 40 to 50 on the Shore hardness scale. It is preferable for one casing to have protruding ribs, while the other casing has corresponding grooves; by compressing the silicone ring in these grooves, IP68-level waterproofing can be achieved. It is important to note that the width of the grooves should be slightly larger than the outer diameter of the silicone ring.

The small enclosure is waterproofed; when a small enclosure or a flat panel is embedded within the main enclosure, side-mounted silicone gaskets are typically used. The interference amount is generally set between 0.1 and 0.2 mm, and the hardness of the silicone gasket is approximately 45 on the Shore hardness scale.

The waterproofing of lenses is generally achieved by using double-sided adhesive or dispensing glue for fixation. Double-sided adhesive should typically have a width of at least 1.5 mm to provide effective waterproofing. It is important to maintain pressure on the adhesive for a sufficient period of time. If the width is less than 1.5 mm, it is better to use dispensing glue for fixation. However, in this case, the lens will no longer have waterproofing properties once disassembled.

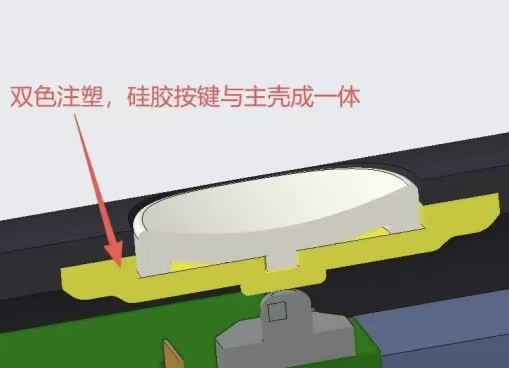
Waterproofing of the buttons: Due to the limited space in smart bracelets, a dual-rubber-ring waterproofing design is commonly used. It is essential that the mating surfaces have a high degree of smoothness; the interference value typically ranges between 0.1 and 0.12. When holding the device, the buttons are usually manufactured using two-color injection molding, with the main casing made of hard plastic and the buttons made of soft plastic.

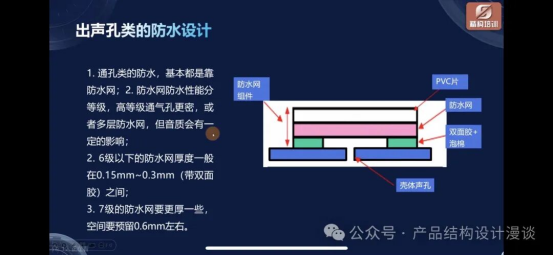
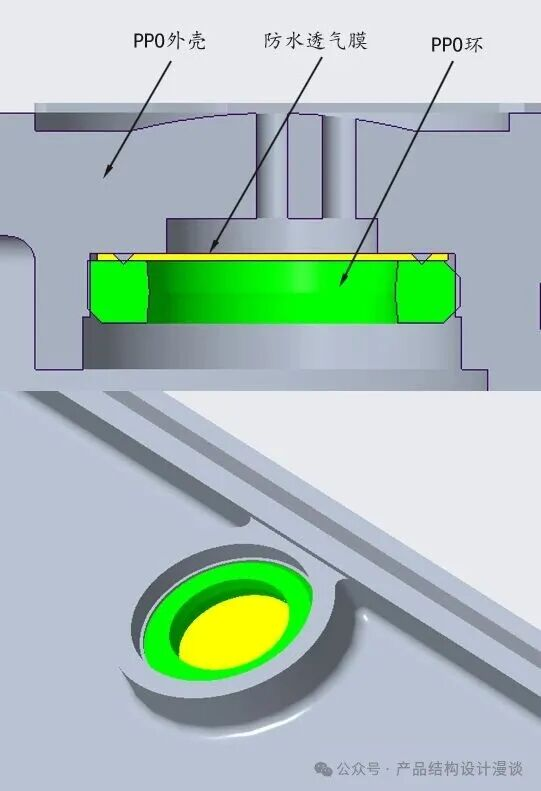
Waterproof and breathable membranes are commonly used in acoustic devices such as speakers. To achieve waterproofing, these membranes are typically equipped with self-adhesive backing, enabling them to meet IPx4 standards. For higher levels of waterproofing, a sandwich structure can be employed, where the breathable membrane is secured in the middle using ultrasonic welding on both the upper and lower layers.
The waterproof design of the charging port plug is typically achieved by using side-pressing soft rubber. If the plug is made entirely of soft rubber, it can achieve an IPx4 rating. However, if the plug consists of a hard material combined with a rubber gasket, or if it is made using two-color injection molding, it can achieve a higher level of waterproofing.
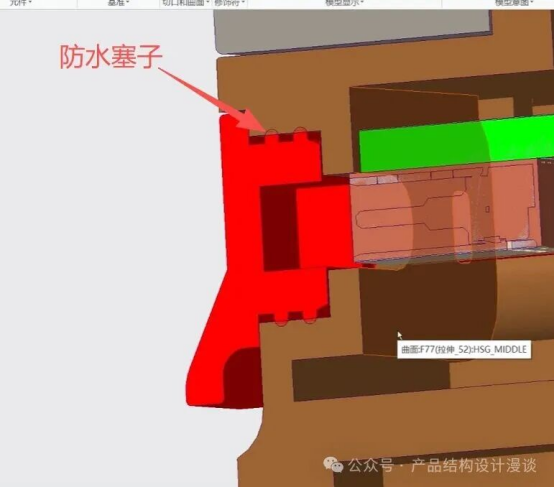
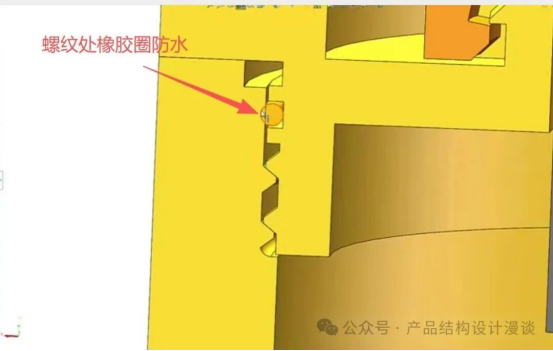
For the waterproofing of threaded connections, one method involves applying pressure to the sealing ring on the front of the cap. Another approach is to add a rubber gasket at the end of the thread, which is then secured in place by applying pressure from the side.
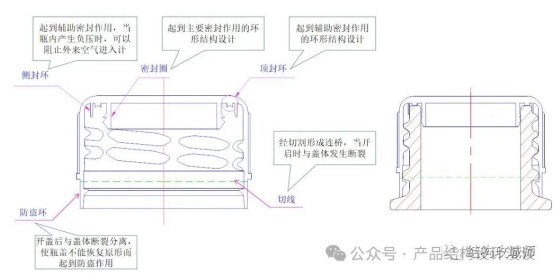
Waterproof design is a systematic endeavor. During the testing process, failures due to aging caused by extreme temperatures are likely to occur. If the product is to operate in a humid environment for extended periods, not only must the external structure be made waterproof, but the internal circuit boards must also be coated with a three-proof paint or a nano-coating. In some cases, it may even be necessary to directly seal the interfaces with adhesive in order to ensure the product’s long-term and reliable performance.


