In today’s connected world, USB has become one of the most important interface standards for computers, consumer electronics, and industrial systems. From charging smartphones to transferring high resolution video and powering professional devices, choosing the right USB cable directly affects performance, stability, and future compatibility. This article explains what USB is, how it works internally, the role of channels and pins, TX and RX transmission, USB connector types, and the new capabilities introduced by USB4.

What Is USB?
USB stands for Universal Serial Bus. It is an industry standard designed to connect computers with peripherals such as keyboards, cameras, storage devices, displays, and industrial equipment. The main goals of USB are simplicity, plug and play operation, and wide compatibility across devices and platforms.
Since its introduction, USB has evolved through multiple generations—USB 2.0, USB 3.0, USB 3.1, USB 3.2, and now USB4—each bringing higher data rates, improved power delivery, and broader functionality. Despite these changes, backward compatibility has always been a core design principle, allowing older devices to work with newer hosts.
The Internal Working Principle of USB
At its core, USB is a host centric serial communication system. A host device (such as a PC or industrial controller) manages all communication, while connected devices respond to the host’s requests.
Data transmission in modern USB standards is based on high speed differential signaling. Instead of sending data over a single wire, USB uses paired signal lines to reduce noise and electromagnetic interference (EMI). This approach is essential for maintaining signal integrity at multi gigabit speeds.
USB protocols define how data is packaged, transmitted, verified, and retransmitted if errors occur. As USB speeds increased, the protocol became more sophisticated, enabling full duplex communication and efficient bandwidth usage.
USB Channels, Pins, and Signal Structure
A USB cable is more than just copper wires. Inside, it contains multiple signal paths, each with a specific role:
Power pins (VBUS and GND): Supply power from the host or charger to the device.
Data pins: Carry the data signals between devices.
Configuration and control pins: Used for orientation detection, role negotiation, and power management (especially in USB Type C).
In USB 3.x and USB4, the cable includes multiple high speed channels (lanes). These lanes operate in parallel to increase total bandwidth. For example, USB 3.0 introduced dedicated SuperSpeed lanes alongside the legacy USB 2.0 pins, allowing backward compatibility while enabling higher performance.
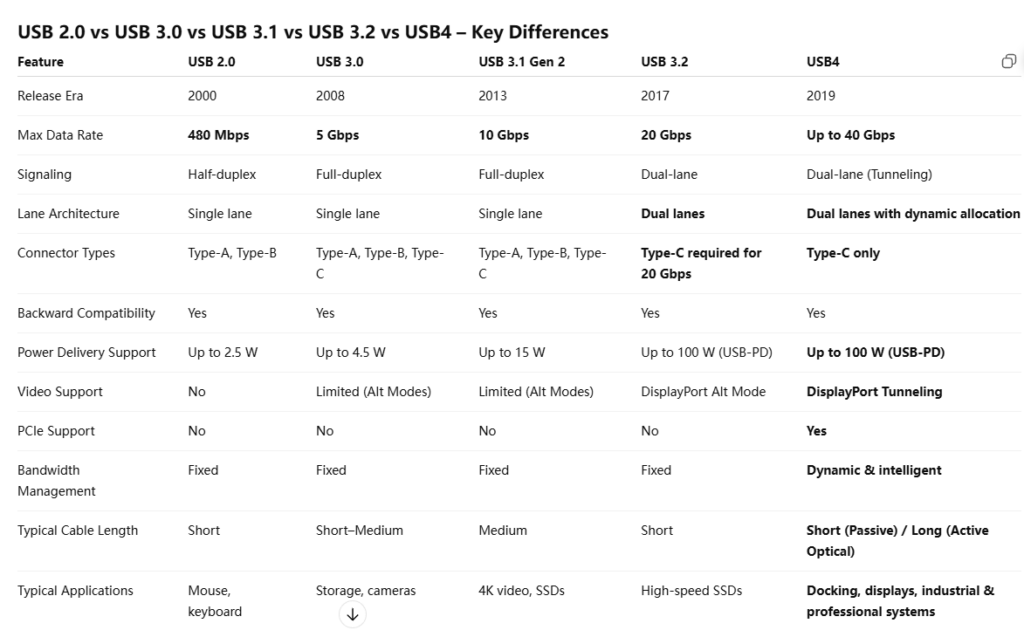
TX and RX: Transmitter and Receiver Explained
In high speed USB communication, data transmission is divided into:
TX (Transmitter): Sends data from the source device.
RX (Receiver): Receives data at the destination device.
Modern USB standards use separate differential pairs for TX and RX, enabling full duplex communication. This means data can be transmitted and received simultaneously, which significantly improves efficiency compared to older half duplex designs.
For long distance or high bandwidth applications, such as active optical USB cables, the TX signal is converted into optical signals, transmitted through fiber, and then converted back to electrical signals at the RX end. This design greatly reduces signal loss and EMI.
USB Interface Types
USB connectors have evolved alongside performance requirements:
USB Type A: The classic rectangular connector, commonly found on computers and chargers.
USB Type B: Often used for printers and industrial equipment.
Mini USB and Micro USB: Compact connectors used in older mobile devices.
USB Type C: The latest and most versatile connector, featuring a reversible design, higher power delivery, and support for multiple protocols.
USB Type C is not a speed standard by itself, but it is the physical interface used by USB 3.2, USB4, and Thunderbolt technologies.

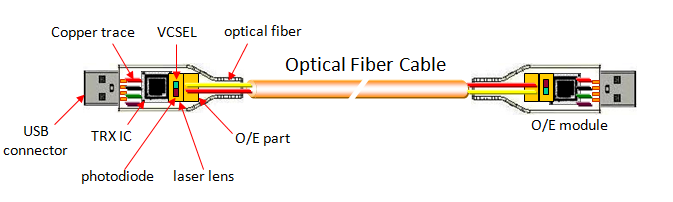
What’s New in USB 4?
USB 4 represents a major shift from previous USB generations. Instead of being just a faster USB, USB 4 is a unified high speed connectivity platform.
Key new features of USB 4 include:
Up to 40 Gbps bandwidth: Ideal for high resolution displays, fast storage, and professional devices.
Multi protocol support: USB 4 can carry USB data, DisplayPort video, and Phttps://elikecorp.com/product/usb-3-1-am-to-micro-b-active-optical-cable-backward-compatible/CIe traffic over a single cable.
Dynamic bandwidth allocation: Bandwidth is intelligently shared between data and display, depending on real time needs.
Exclusive use of USB Type C: Simplifies device design and user experience.
Improved system integration: Fewer ports, fewer cables, and reduced system complexity.
These capabilities make USB 4 especially attractive for OEMs, system integrators, and industrial applications that demand performance, reliability, and future scalability.
Choosing the Right USB Cable
Not all USB cables are created equal. To achieve the expected performance, the cable must support the required USB generation, power rating, and application environment. For high speed or long distance installations, active or optical USB cables may be necessary.
When selecting a USB cable, consider data rate requirements, power delivery needs, connector type, and future upgrade plans. Choosing the right USB cable ensures stable operation today and compatibility tomorrow.
Why choose smartavlink?
Choosing Smartavlink means choosing reliability, expertise, and long-term value. With years of deep focus on high-speed interconnect solutions such as USB, HDMI, DisplayPort, and Active Optical Cables, we understand not only the standards, but also the real-world challenges faced by OEMs, system integrators, and industrial customers.
From signal integrity and EMI control to long-distance transmission and system compatibility, every Smartavlink product is engineered, tested, and validated for stable performance. We offer flexible OEM/ODM customization, strict quality control, and responsive technical support—helping our customers reduce risk, shorten development cycles, and bring dependable products to market with confidence.


